What is oral pathology?
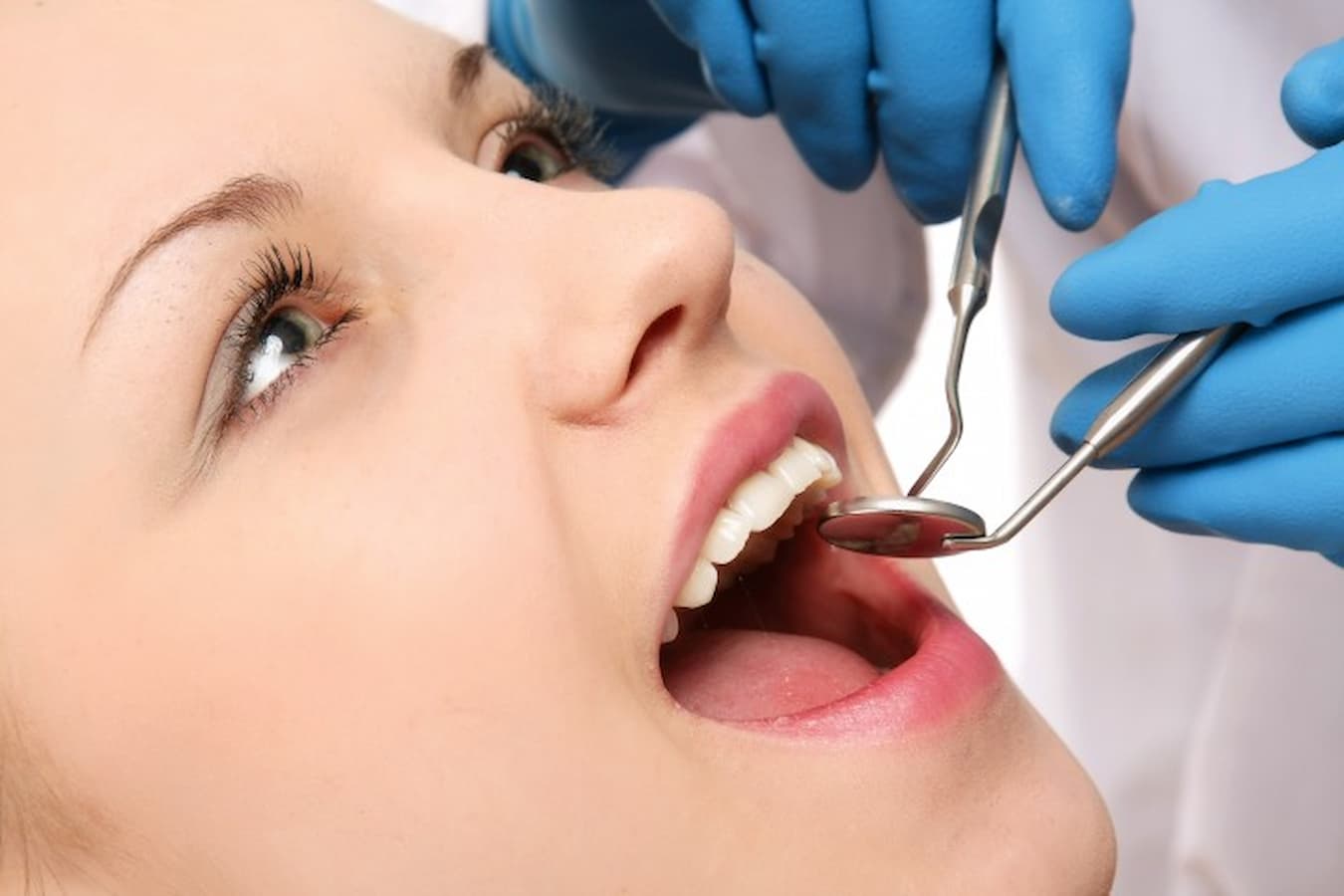

Before performing the biopsy, the oral surgeon will visually inspect the area of concern. This, too, gives the specialist important information that can be used in determining the patient’s specific diagnosis. Imaging, such as an x-ray or MRI, may also be ordered to give the surgeon more in-depth views of the targeted area.
The oral surgery needed for the biopsy is relatively simple. The surgeon will remove a small sample of tissue for further analysis. Biopsies typically are performed in outpatient settings, and the patient usually will need only a local anesthetic.
The conditions identified through oral pathology may be either benign or malignant. Your surgeon will inform you of the results of testing and explain the diagnosis to you.
When oral pathology helps to identify serious conditions, such as oral cancer, it can truly be a life-saving endeavor. Oral cancer is most treatable in its earliest stages, so if you notice any strange spots on your gum or tongue, bring them to your dentist’s attention as soon as possible. These include unusual red or white spots, sores that will not heal and persistent lumps.
The recommended treatment, whether the condition is cancerous or not, may require additional oral surgery to remove remaining diseased tissue. Your surgeon will educate you on the treatment plan, including the risks and benefits of each treatment option.
Oral pathology can help patients get a diagnosis and effective treatment for a variety of oral diseases. If you have noticed a symptom of concern, contact our office to learn more about this process and schedule an appointment to get started on the path to diagnosis and treatment.